Cesarean Delivery
Home / Cesarean Delivery
Home / Cesarean Delivery
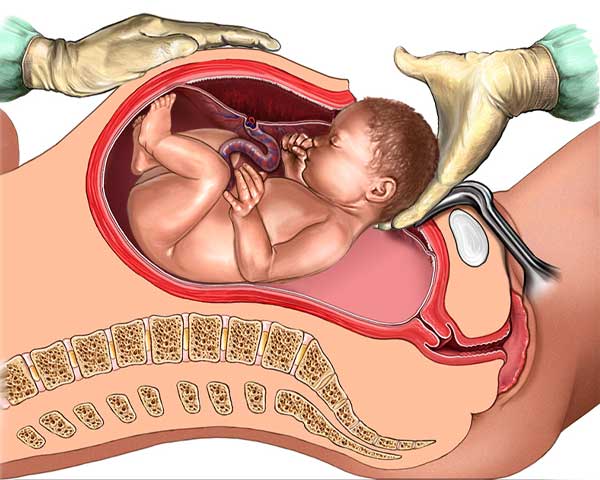
Cesarean delivery, often shortened to C-section, is a surgical procedure to deliver a baby through incisions in the mother's abdomen and uterus. It's a safe and common procedure, used when vaginal delivery isn't possible or advisable for the health of the mother or baby.
There are many reasons why a C-section might be recommended, including:
The two main types of C-sections are:
Low-transverse C-section: This is the most common type, with a horizontal incision made just below the bikini line.
Classical C-section: This less common type involves a vertical incision through the abdomen. It's usually only used in emergencies.
A C-section is typically performed in a hospital operating room. You'll usually receive regional anesthesia, like an epidural, which numbs the lower half of your body. In some cases, general anesthesia might be used if time is crucial.
The surgeon will make the incision, deliver the baby, and then close the incisions with stitches or staples. The entire procedure usually takes around 45 minutes to an hour.
After a C-section, you'll spend a few hours in recovery, then be moved to a postpartum room. You can expect some pain and discomfort, but pain medication will be available. You'll likely need to stay in the hospital for 2-3 days.
Recovery from a C-section takes longer than from a vaginal delivery. You'll need to rest for several weeks and avoid strenuous activity. It's important to listen to your body and take things slowly.
While C-sections are major surgeries, they offer several benefits:
C-sections are major surgeries, so it's important to weigh the risks and benefits before making a decision. Some potential risks of C-sections include:
If you're facing the possibility of a C-section, it's important to talk to your doctor about your specific situation. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of both C-section and vaginal delivery and make the best decision for you and your baby.